Explain How Liquid Chromatography Separates Compounds of Different Polarity
It uses designed stationary phases instead of bare alumina or silica particles. Eluent For liquids the polarity of a solvent is defined as its ability to dissolve polar organic compounds.
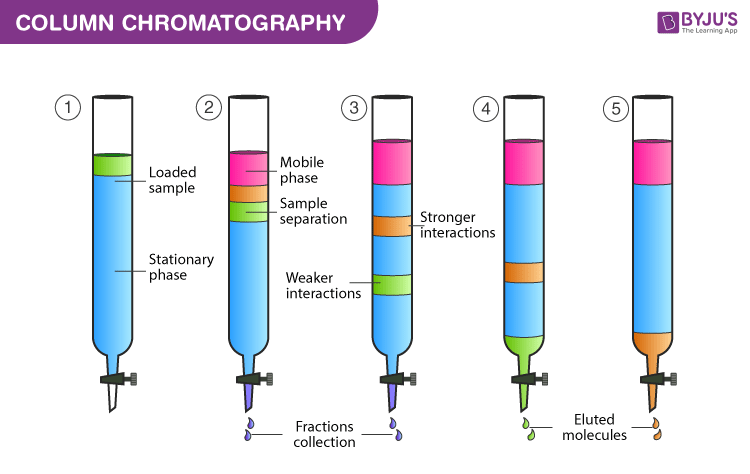
Column Chromatography Principle Procedure Applications Elution In Chromatography
Separation in column chromatography relies on differences.

. A stationery phase is the solid eg. A type of adsorption chromatography is column chromatography. Nonpolar eluents are used first to move the least polar analyte compounds then.
Reverse phase chromatography. The phase the moves. Chromatography is an important biophysical technique that enables the separation identification and purification of the components of a mixture for qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Chromatography is a method of separating substances completely. We know that HPLC separation occurs based on the interaction between the compound with the stationary and mobile phases but in a gas chromatographic analysis separation occurs based on the volatility of each compound. We leverage these differences to distribute molecules between a stationary phase and a mobile phase.
Ad Luer Lock Non-jacketed bed volume 8 mL ID. It uses an adsorbent called silica gel to separate several organic. Silica that stays inside the column.
Eluent is the fluid that enter into the column. Explain how chromatography separates compounds using the terms. In normal phase chromatography increasing polarity results in increased retention and higher selectivity.
Or longer stainless steel tube packed with adsorbent usually a liquid phase on an inert solid support and put in a temperature controlled. The less polar compounds are eluted first in normal phase chromatography whereas more polar ones last. Reverse phase chromatography is also used for HPLC.
Gas chromatography still uses stationary and mobile phases like HPLC but the mobile phase is typically an unreactive or inert. In the case of NPLC as a mode of liquid solid chromatography LSC the stationary phase is polar silica alumina or polar-bonded phase and the mobile phase is nonpolar hexane heptane etc. When it comes to liquid chromatography the predominant retention mode is reversed phase chromatography.
Compounds dissolved into the solvent spend more time moving in the mobile phase Non-polar solvents can only dissolve. The solvent used for chromatography will be selected based on the polarity of the substances in the mixture you want to separate. Normal Phase Chromatography is generally used to separate chiral compounds cis-trans isomers geometric isomers and water-sensitive compounds.
The basic principle is they all have a stationary phase a solid or a liquid supported on a solid and a mobile phase a liquid or a gas which carries the components of the mixture with it The mobile phase flows through. IMFs dynamic equilibrium polarity. However you will see that if two compounds have similar boiling points but very different polarities they can be separated by polarity via GC.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION A reverse-phase column surface is nonpolar and nonpolar compounds are more attracted to the nonpolar surface in the presence of water and organic mobile phase. Prior to the flowing solvent reaching the farther paper edge both the solvents are evaporated and the location of the separated component can be identified generally by the application of reagents that produce colored compounds with the separated substances. Eluents are typically used in order of polarity.
Chromatography is a method for separating mixturesbased on differences in the speed at which they migrate over or through a stationary phase. Adsorption mechanism involves adsorption of an analyte by its polar groups on the polar active sites of the stationary phase. Then the separated components appear as individual spots on the solvents path.
The term chromatography is derived from Greek chroma meaning colour and graphein meaning to write. Reverse-phase chromatography separates compounds by how polar and nonpolar they are in relation to each other. Underline each time the first time it is used.
There are several types of chromatography of which column chromatography is the most frequently used in laboratories that deal with organic compounds. Published August 29 2016. This is a solid - liquid technique in which the stationary phase is a solid mobile phase is a liquid.
The more polar the mobile phase the faster all compounds run through the stationary phase. Like Normal Phase Chromatography HILIC uses a polar stationary phase and a non-polar yet water-miscible mobile phase. The gas chromatograph contains a long 6 ft.
In reversed phase chromatography increasing polarity results in reduced retention. May 8 2014. Stationary phase mobile phase distribution or partition solubility or affinity.
The mobile phase consists of liquid solvents eluents of different polarities that move and separate analyte compounds through the stationary phase. There are different ways to separate mixtures for example by filtration crystallisation distillation or chromatography. The method chosen depends upon the type of mixture.
Underline each time the first time it is used. Opposite of normal phase polarity reverse phase uses a polar liquid mobile phase and non-polar stationary phase to separate the most polar compounds followed by compounds with lower polarity. IMFs dynamic equilibrium polarity.
Chromatography is the technique for the separation purification and testing of compounds. But because molecules are so different its not possible to have a single method that works for all. X L 10 cm x 10 cm.
A mobile phase is the solvent that moves through the column. Ion Exchange Chromatography is generally used to separate compounds differing in functional groups. HILIC fills a need in analytical separations and is used for the separation of very polar molecules like acids bases and zwitterions.
The principle of column chromatography is based on differential adsorption of substance by the. In liquidsolid or adsorption chromatography the chemical components are adsorbed on the hydroxyl sites of polar adsorbents such as powdered silica and alumina packed in the column and elution is performed with solvents of increasing polarity. In this process we apply the mixture to be separated on a stationary phase solid or liquid and a pure solvent such as water or any gas is allowed to move slowly over the.
Proteins can be purified based on characteristics such as size and shape total charge hydrophobic groups present on the surface and binding. A chromatography is a physical method of separation while chromatograph is an equipment to separates mixture of compounds into its components. Can be gas or liquid solvent.
Column chromatography is one of the most useful methods for the separation and purification of both solids and liquids. 55 HPLC is a variant incorporating high pressure pumps and automated metering units to change the gradient of the mobile. Molecules vary in size charge polarity and solubility.
The Separation Of Compounds Of Different Polarity. Chromatography is a technique used to separate individual components in a mixture.
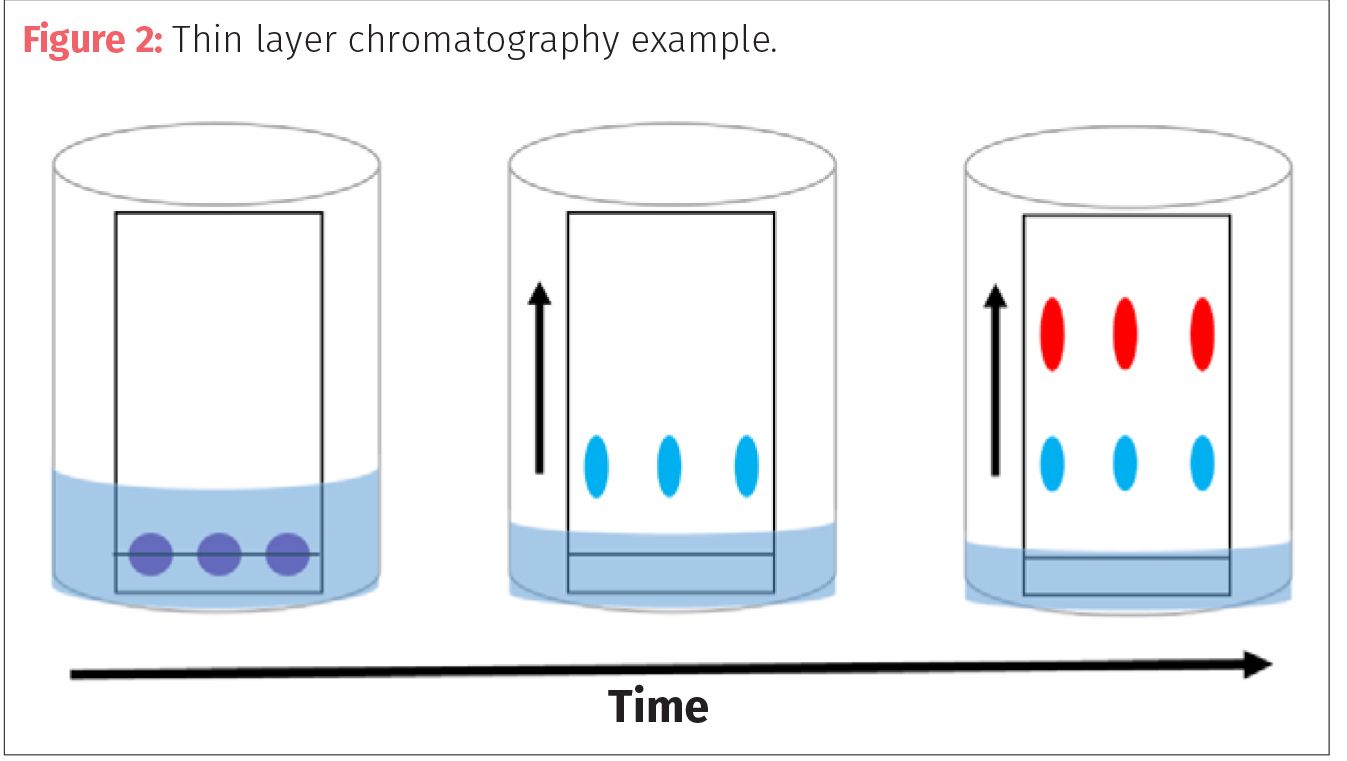
Looking With Light Understanding The Principles Of Analytical Liquid Chromatography

Principles Of Chromatography Stationary Phase Article Khan Academy
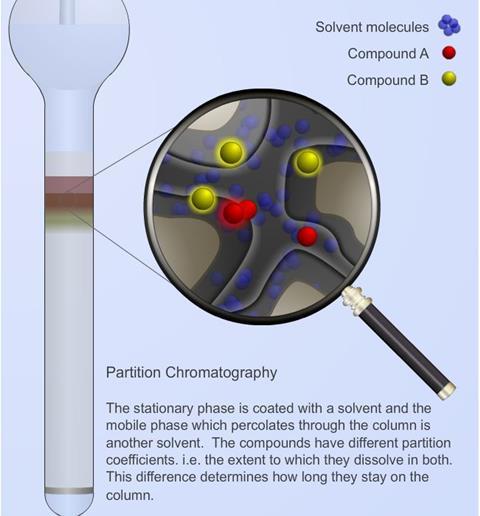
Chromatography Resource Rsc Education

Principles Of Chromatography Stationary Phase Article Khan Academy
No comments for "Explain How Liquid Chromatography Separates Compounds of Different Polarity"
Post a Comment